Choosing the right air conditioner size is crucial for comfort, efficiency, and cost savings. An oversized unit wastes energy, causes humidity issues, and wears out faster due to frequent cycling. An undersized unit struggles to cool effectively, running constantly and driving up utility bills.
Quick Steps to Determine the Right Size:
- Measure Your Space: Calculate the square footage by multiplying the room’s length by its width. Adjust for ceiling height, open floor plans, or connected spaces.
- Estimate Cooling Capacity (BTUs): Use the guideline of 20 BTUs per square foot. Adjust for sunlight, kitchens, additional occupants, and upper floors.
- Convert BTUs to Tonnage: Divide the BTU requirement by 12,000 to determine the tonnage needed.
- Get a Manual J Load Calculation: For precise results, consult a professional to account for insulation, windows, and local climate.
Example: A 300 sq. ft. room typically requires around 6,000 BTUs, but factors like sunlight or high ceilings may increase this need.
Proper sizing ensures consistent temperatures, efficient operation, and lower energy bills. Avoid guessing – use these steps or consult a professional for accurate results. Our team provides comprehensive cooling services to ensure your system is perfectly matched to your home.
WHAT AIR CONDITIONER SIZE DO I NEED? How To Size Air Conditioner For Your House
sbb-itb-b5c10b1
Step 1: Measure Your Space
Getting the right air conditioner starts with accurate measurements of your space.
How to Calculate Square Footage
If your room is a standard rectangle, the calculation is simple: length times width in feet. For example, a living room that’s 15 feet by 20 feet would total 300 square feet.
If your measurements include inches, convert them to decimal form first. For instance, a room that’s 12 feet 6 inches long should be calculated as 12.5 feet. Use these simple conversions: 3 inches equals 0.25 feet, 6 inches equals 0.5 feet, and 9 inches equals 0.75 feet.
For spaces with irregular shapes, divide the area into smaller, manageable shapes like rectangles, squares, or triangles. Calculate the area of each section – for triangles, multiply the base by the height and divide by two – then add them up to get the total square footage.
Account for Room Features
Square footage is just one piece of the puzzle. Ceiling height matters too. Most BTU estimates assume a 9-foot ceiling. If your ceilings are higher, you’ll need more cooling power – typically 10% to 25% more capacity.
Open floor plans also require extra consideration. If two rooms are connected without a door, combine their square footage. The air conditioner will need to cool both spaces as one zone. The same principle applies to large archways or hallways – treat these connected areas as a single space.
Once you’ve measured and accounted for these factors, you’ll be ready to calculate the BTU requirements for your space using a specialized tool.
Step 2: Determine Cooling Capacity Using BTUs
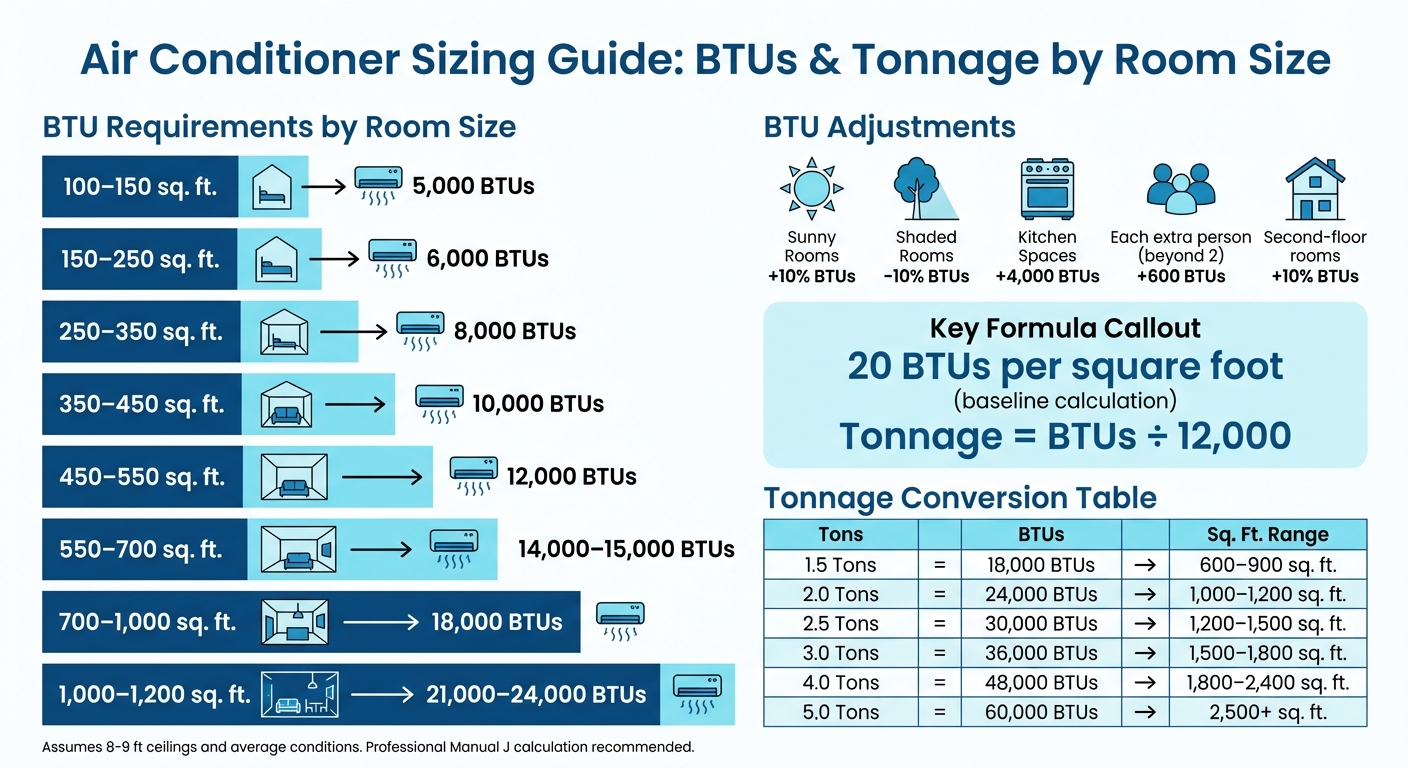
Air Conditioner BTU and Tonnage Requirements by Room Size
A BTU, or British Thermal Unit, measures how much heat an air conditioner can remove in an hour. Think of it as the energy needed to raise or lower the temperature of one pound of water by 1°F. For context, a 12,000 BTU unit can remove enough heat in an hour to melt 114 pounds of ice.
Getting the BTU calculation right is critical. Mike Lea, Co-owner of Lea Heating & Air Conditioning, points out that improperly sized units – whether too large or too small – can lead to higher energy bills and reduced comfort. In fact, a Department of Energy study revealed that nearly half (47%) of residential AC systems are oversized by at least half a ton.
BTU Requirements by Room Size
Once you understand BTUs, you can use them to estimate the cooling capacity you’ll need based on your room size. A common guideline is 20 BTUs per square foot of living space. Here’s a breakdown to help you calculate:
| Room Size (sq. ft.) | Recommended Capacity (BTUs) |
|---|---|
| 100–150 | 5,000 |
| 150–250 | 6,000 |
| 250–350 | 8,000 |
| 350–450 | 10,000 |
| 450–550 | 12,000 |
| 550–700 | 14,000–15,000 |
| 700–1,000 | 18,000 |
| 1,000–1,200 | 21,000–24,000 |
These estimates assume standard 8-foot ceilings and average conditions. For example, a 300-square-foot living room would typically require around 6,000 BTUs.
But don’t stop here – adjustments may be needed based on your room’s unique characteristics.
Adjust BTUs for Room Characteristics
Several factors can influence your BTU needs:
- Sunlight: Add 10% more BTUs for rooms with significant sun exposure, while heavily shaded spaces can reduce the requirement by 10%.
- Kitchens: Cooking appliances generate extra heat, so add 4,000 BTUs when cooling a kitchen.
- Occupants: Standard calculations assume two people. For each additional person, add 600 BTUs.
- Second-Floor Rooms: Heat naturally rises, so increase the BTU estimate by 10% for upper-level spaces.
"If it’s too big, it will cycle on and off too frequently and fail to maintain comfort; if it’s too small, it won’t run enough and can lead to humidity issues in the home."
- David Fowler, Owner of Family Heating and Air
Oversized units tend to short cycle, which means they turn on and off too quickly, failing to properly remove moisture. Undersized systems, on the other hand, run constantly, leading to higher energy costs and faster wear and tear.
This customized BTU calculation provides a solid starting point before converting to tonnage and selecting your final unit and scheduling a professional HVAC installation.
Step 3: Convert BTUs to Tonnage
Once you’ve calculated the required BTUs for your space, the next step is to convert that number into tonnage. To do this, divide the BTU figure by 12,000. Why 12,000? Because one ton of cooling capacity equals 12,000 BTUs per hour. This measurement has nothing to do with the physical weight of the air conditioner. Instead, it originates from an old refrigeration standard: one ton represents the amount of heat needed to melt 2,000 pounds of ice over 24 hours, which equals 12,000 BTUs per hour. For example, if your cooling needs are 24,000 BTUs, you’d need a 2-ton unit (24,000 ÷ 12,000 = 2).
Residential central air conditioning systems generally range between 1.5 and 5 tons, with manufacturers producing units in half-ton increments like 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, and so on. For a typical 2,000-square-foot home, a 3.5- to 4-ton unit is often sufficient, although factors like insulation quality and local climate can influence the exact sizing.
| Unit Size (Tons) | Cooling Capacity (BTUs) | Typical Home Size (Sq. Ft.) |
|---|---|---|
| 1.5 Tons | 18,000 BTUs | 600 – 900 |
| 2.0 Tons | 24,000 BTUs | 1,000 – 1,200 |
| 2.5 Tons | 30,000 BTUs | 1,200 – 1,500 |
| 3.0 Tons | 36,000 BTUs | 1,500 – 1,800 |
| 4.0 Tons | 48,000 BTUs | 1,800 – 2,400 |
| 5.0 Tons | 60,000 BTUs | 2,500+ |
How to Read Air Conditioner Model Numbers
Air conditioner model numbers can offer quick insight into the unit’s cooling capacity. Most manufacturers include the BTU rating as a two-digit number within the model number, representing thousands of BTUs. Look for numbers like 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, or 60 on the outdoor unit’s nameplate. For instance:
- In the model number 4TTV8X36A1000A, the "36" signifies 36,000 BTUs. Divide 36 by 12, and you get a 3-ton unit.
- Similarly, a model like 4A7V0X60 includes "60", which represents 60,000 BTUs, equating to a 5-ton system.
This simple check can help ensure your replacement unit matches the cooling requirements you’ve determined. However, don’t automatically assume the unit currently installed in your home is the correct size. As Anne Fonda, Content Writer at Trane Technologies, points out:
"bigger isn’t always better. Accurate AC sizing is crucial to your home’s comfort and the ability of your cooling system to work efficiently".
Since factors like insulation and window quality can change over time, it’s always a good idea to consult a professional to verify your needs before purchasing a new unit. With your system’s tonnage confirmed and the model number decoded, you’re prepared to proceed to professional load calculations in Step 4.
Step 4: Get a Manual J Load Calculation

When it comes to determining your home’s heating and cooling needs, square footage and basic BTU estimates only scratch the surface. For precise results, a Manual J load calculation is essential. This ANSI-approved ACCA standard goes beyond generic estimates, measuring how much heat your home loses in winter and gains in summer to create a detailed energy profile.
This method takes into account over 30 different factors, such as insulation levels, window orientation, ceiling height, local climate, and even internal heat sources. For instance, a west-facing 3’x5′ window without shading can add up to 2,000 BTU/hr to your cooling load. Better insulation – like R-38 compared to R-13 – can slash BTU needs by as much as 40%. Location also plays a big role: a 2,000-square-foot home might need 4 tons (48,000 BTU/hr) of cooling in Miami, FL, but only 2 tons (24,000 BTU/hr) in Seattle, WA. This detailed calculation ensures your system is tailored to your home’s unique requirements.
As Kate Pospisil from Modernize explains:
"There is no accurate way to size a heating or cooling system without a Manual J. It is the only method recognized by building codes, utilities, and equipment manufacturers because it evaluates the home itself – not just its square footage."
Benefits of Professional Sizing
While rough estimates might give you a starting point, a Manual J calculation provides the exact measurements needed for proper system sizing. This level of precision ensures your HVAC system is neither too large nor too small for your home.
Why does this matter? Oversized systems tend to short cycle, while undersized ones run non-stop, both of which can lead to higher energy bills. An oversized unit, for example, can waste 20% to 40% more energy than one that’s properly sized, while also causing uneven temperatures and humidity issues. It’s no surprise that many building codes require a Manual J calculation before installation.
Certified technicians use ACCA-approved software like Wrightsoft Right-J or CoolCalc to perform these calculations. Always ask for a copy of the Manual J report before making any American Standard air conditioner or other equipment purchases. Be cautious of contractors who rely solely on outdated rules like "1 ton per 500 square feet", as these ignore critical factors like insulation and window placement. Also, verify that your technician uses data specific to your home rather than relying on generic software defaults.
Step 5: Consult Eco Temp HVAC for Expert Help

Once you’ve done the groundwork with calculations, it’s time to bring in certified professionals to refine your air conditioner sizing. While the earlier steps help you understand the basics, expert input ensures your system operates at its absolute best.
Eco Temp HVAC: Certified Technicians You Can Rely On
Eco Temp HVAC proudly serves the Chicagoland area with a team of certified professionals. As a Mitsubishi Diamond Elite Contractor, they’ve earned top-tier recognition from the manufacturer, which allows them to provide an impressive 12-year warranty on Mitsubishi products – far exceeding typical warranties. They’re also certified as a Navien Service Specialist and an American Standard Customer Care Dealer, showcasing their expertise across a range of high-efficiency systems.
Their technicians go beyond surface-level assessments by performing Manual J load calculations, a detailed process typically included with their installation packages. This evaluation considers all aspects of your home, including insulation, window placement, ductwork condition, and the local climate. By focusing on these factors, Eco Temp HVAC ensures the recommended system isn’t just based on square footage but tailored to your home’s specific cooling demands. This thorough approach bridges the gap between estimation and peak system performance.
Reach Out to Eco Temp HVAC for a Consultation
Eco Temp HVAC offers fast, reliable service throughout Chicagoland, including areas like Chicago, St. Charles, Bartlett, Lemont, Downers Grove, and Palatine. Whether you’re looking for a split system, ductless mini-split vs. traditional central HVAC, or packaged unit, their technicians will guide you toward the best option for your home’s design and cooling needs. With precise calculations in hand, they’ll ensure your air conditioner is the perfect fit for your home.
Ready to get started? Visit ecotemphvac.com to schedule your personalized assessment. With efficient systems available around the clock, Eco Temp HVAC is here to help you find the right size air conditioner – so you can enjoy comfort and energy savings all year long.
Conclusion
Choosing the right air conditioner size starts with understanding your space, calculating the required BTUs, and considering the unique features of your home. A general guideline is to allocate about 20 BTUs per square foot of living space. However, this estimate doesn’t account for details like insulation, window placement, or appliances that generate heat.
Getting the size wrong can lead to problems. Oversized units waste energy and cycle on and off too frequently, while undersized units struggle to keep up, running constantly and driving up utility costs. Both scenarios can lead to higher energy bills and faster wear on your system.
For the most accurate results, a Manual J load calculation is the gold standard. This professional evaluation eliminates guesswork, ensuring your system is perfectly tailored to your home’s needs. Keep in mind, simply replacing an old unit with the same size might not be the best choice – upgrades like new windows or added insulation could have changed your cooling requirements.
If you’re ready for a system that delivers comfort and efficiency, Eco Temp HVAC’s certified technicians in the Chicagoland area can help. Their expertise in Manual J assessments ensures your air conditioner is properly sized to maintain consistent temperatures, reduce energy waste, and handle humidity effectively. A well-sized system means lower bills, reliable performance, and a comfortable home for years to come.
FAQs
Can I use one AC for connected rooms?
Yes, it’s possible to cool multiple connected rooms using just one air conditioner, but it takes careful planning to make it work effectively. To spread the cool air, you can use fans strategically – position them to direct airflow into adjoining spaces. Ceiling fans are also a great option for improving air circulation throughout the rooms.
For more precise temperature control, you might want to look into ductless mini-split systems, which allow you to cool specific areas more efficiently. Another crucial step is sealing and insulating the rooms. This prevents air leaks and helps maintain a consistent temperature, ensuring that the cool air stays where you need it. By combining these methods, you can make the most out of a single AC unit.
How do high ceilings change BTU needs?
High ceilings mean your air conditioner has to work harder. Why? Because they increase the volume of air that needs cooling. With more space to regulate, your HVAC system requires a higher cooling capacity – measured in BTUs (British Thermal Units) – to keep the entire area at a comfortable temperature. Essentially, the taller the ceiling, the more air mass there is to cool.
When do I need a Manual J calculation?
A Manual J calculation is a critical step when figuring out the heating and cooling needs of your home, especially during an HVAC replacement or new construction. This process ensures the system is the right size to avoid issues like inefficiency, discomfort, or short cycling. It takes into account factors such as the size of your home, insulation levels, window types, and local climate. By addressing these variables, the calculation helps achieve better comfort, energy savings, and overall system performance.











