Heat pumps are a reliable and efficient way to heat homes in freezing temperatures, even in regions with harsh winters like Chicagoland. Unlike systems that burn fuel, heat pumps transfer heat from outdoor air into your home using electricity, making them up to 400% efficient. Modern cold climate models work effectively in temperatures as low as -15°F to -20°F, maintaining at least 70% of their heating capacity at 5°F.
Key Features at a Glance:
- Efficiency: Up to 400%, far surpassing gas furnaces (~92%).
- Cold Performance: Operates reliably at -15°F to -20°F, with a COP ≥ 1.75 at 5°F.
- Dual Functionality: Provides both heating and cooling in one system.
- Advanced Technology: Includes variable-speed inverter compressors and automated defrost cycles.
Why Choose a Heat Pump?
- Lower Costs: Uses less energy compared to propane, fuel oil, or electric resistance heating.
- Eco-Friendly: Reduces emissions, especially as electricity grids shift to renewables.
- Reliability: Cold climate models handle sub-zero conditions with features like defrost cycles and advanced compressors.
Proper installation and regular maintenance are critical to maximizing performance. Certified professionals can ensure your system is correctly sized and installed for your home’s needs. With federal tax credits covering up to 30% of installation costs, heat pumps are an efficient, cost-effective solution for winter heating.
Cold Climate Heat Pumps – Warm homes on the coldest days
sbb-itb-b5c10b1
Cold Climate Heat Pump Features
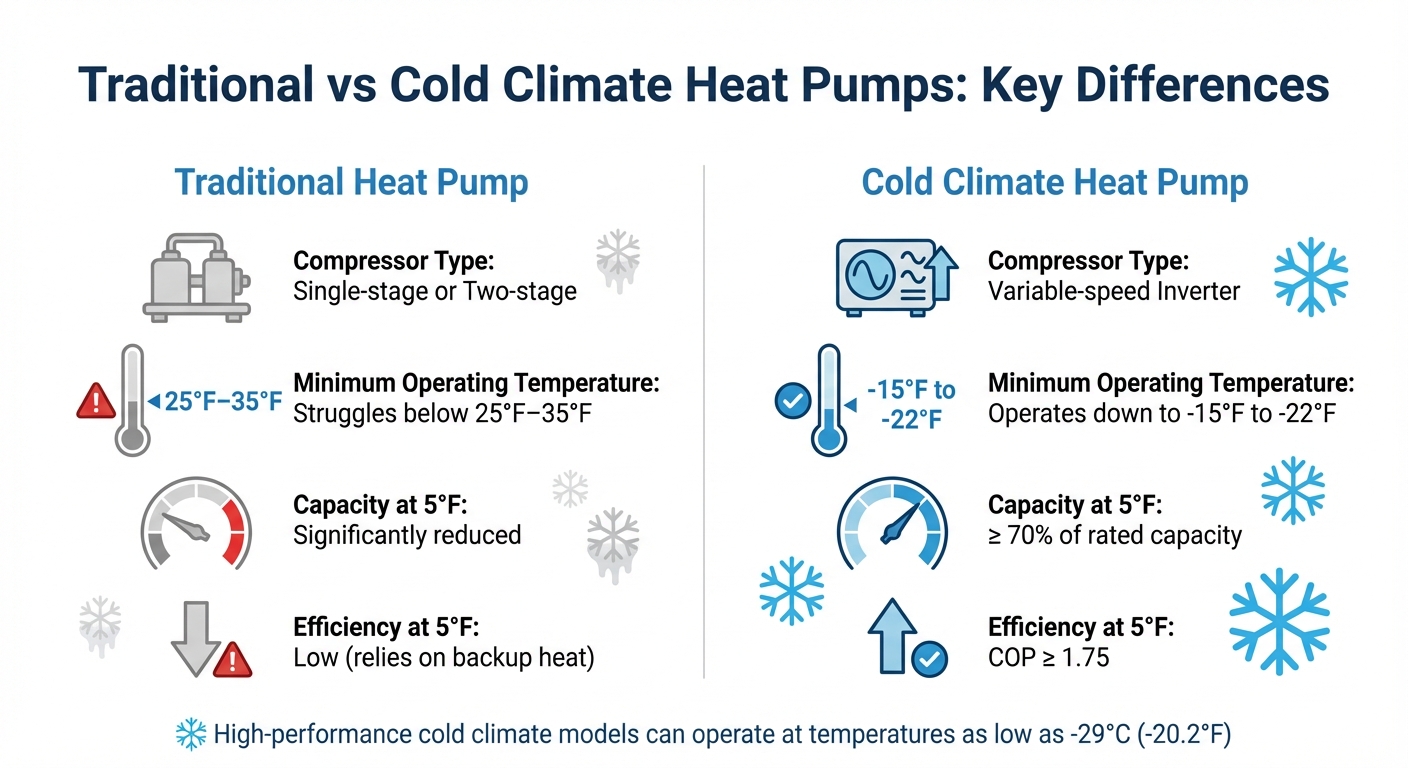
Traditional vs Cold Climate Heat Pump Performance Comparison
Cold climate heat pumps are designed with advanced engineering to extract heat from freezing air, ensuring dependable warmth even during Chicagoland’s harshest winters. Here’s how they do it:
Variable-Speed Inverter Compressors
The heart of a cold climate heat pump is its variable-speed inverter compressor. Unlike traditional single-stage compressors that either run at full capacity or shut off, these compressors adjust their speed to match heating demands. This not only reduces wear and tear but also maintains consistent indoor temperatures. Curtis Herchenbach, Owner of Herchenbach Mechanical, highlights their efficiency:
Today’s cold-climate models can deliver 100% heating capacity down to 0°F and may be two to three times more efficient than older units.
Additionally, these systems use defrost cycle technology to maintain optimal performance in icy conditions.
Defrost Cycle Technology
When outdoor coils freeze, cold climate heat pumps rely on automated defrost cycles to keep running efficiently. Sensors detect frost buildup and trigger the system to reverse its operation temporarily, sending warm refrigerant to the outdoor coil to melt the ice. This process typically takes 5–15 minutes, with the coil reaching 57°F. To speed up the process, the outdoor fan usually pauses, and backup electric heat strips may activate to prevent cold air from entering the home. David Flemm, Owner of Cool Zone Air Conditioning & Heating, explains:
The frost will make it difficult to extract heat from the air. In turn, it needs to melt off the frost to allow the heat pump to operate normally.
This feature ensures the system stays efficient even in freezing weather.
Performance in Sub-Zero Temperatures
Cold climate heat pumps are built to perform under extreme conditions. ENERGY STAR-certified models must retain at least 70% of their rated heating capacity and achieve a Coefficient of Performance (COP) of at least 1.75 at 5°F. Many advanced models surpass these requirements, with COP values ranging between 2.1 and 2.4 at 5°F.
| Feature | Traditional Heat Pump | Cold Climate Heat Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Compressor Type | Single-stage or Two-stage | Variable-speed Inverter |
| Min. Operating Temp | Struggles below 25°F–35°F | Operates down to -15°F to -22°F |
| Capacity at 5°F | Significantly reduced | ≥ 70% of rated capacity |
| Efficiency at 5°F | Low (relies on backup heat) | COP ≥ 1.75 |
Some high-performance models even feature compressor cut-out temperatures as low as -29°C (-20.2°F), allowing them to operate in conditions that would overwhelm standard systems. These advancements make cold climate heat pumps a reliable choice for enduring Chicagoland’s winter challenges.
Selecting a Heat Pump for Cold Weather
Performance Specifications to Review
To ensure your heat pump can handle Chicagoland’s harsh winters, focus on three key performance metrics: HSPF2, COP at 5°F, and capacity ratio. These measurements help gauge how efficiently and reliably the unit will perform in freezing conditions.
- HSPF2 (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor 2): This measures the system’s seasonal efficiency. ENERGY STAR standards recommend a minimum of 8.1 for ducted systems and 8.5 for ductless units.
- COP (Coefficient of Performance) at 5°F: This metric evaluates efficiency in freezing temperatures. ENERGY STAR requires at least 1.75, but top-performing models often reach between 2.1 and 2.4.
- Capacity Ratio: This shows how much heating capacity the unit retains at 5°F compared to its output at 47°F. Look for models that maintain at least 70% of their capacity.
It’s also important to check the manufacturer’s extended performance data. This will confirm the unit’s maximum heating output at local design temperatures, which in Chicagoland usually range from 0°F to 5°F. For extreme conditions, choose a model that operates effectively at temperatures as low as -15°F to -26°F, as indicated by its compressor cut-out temperature.
Cold Climate Heat Pump Models
Several leading manufacturers like Mitsubishi Electric, Carrier, Trane Technologies (American Standard), Bosch, Daikin, Lennox, LG, Midea, and Rheem are part of the Department of Energy’s Cold Climate Heat Pump Challenge. These brands have designed systems specifically for low-temperature performance.
For detailed comparisons, the Northeast Energy Efficiency Partnerships (NEEP) maintains a "Cold Climate Air Source Heat Pump List", which includes extended performance data for thousands of models. This resource makes it easier to find a heat pump tailored to your needs.
| Specification | ENERGY STAR Minimum | DOE Challenge Target |
|---|---|---|
| HSPF2 (Ducted) | ≥ 8.1 | Higher efficiency goals |
| HSPF2 (Ductless) | ≥ 8.5 | Higher efficiency goals |
| COP at 5°F | ≥ 1.75 | 2.1–2.4 (24,000–65,000 BTU/h) |
| Capacity at 5°F | ≥ 70% of rated capacity | Enhanced performance |
| Cut-out Temperature | Varies | -15°F to -26°F operation |
Professional Installation Requirements
Even the most advanced heat pump won’t deliver peak performance without proper installation. Certified technicians use tools like ACCA Manual J and Manual S to accurately size and select equipment that matches your home’s heating requirements. This ensures the system operates efficiently, even during extreme weather.
A blower door test is often recommended to measure air leakage in your home. This prevents oversizing the unit based on estimates alone. Additionally, professional installers assess whether your home needs weatherization improvements before installation, which can further enhance efficiency and comfort.
For example, Eco Temp HVAC’s certified technicians, including Mitsubishi Diamond Elite Contractors, specialize in precise sizing and installation. They also offer extended warranties, such as 12-year coverage on Mitsubishi products, ensuring dependable performance and peace of mind. Proper installation is the key to unlocking the full potential of your heat pump in cold weather.
Installation and Winter Maintenance
System Sizing and Unit Placement
Once you’ve chosen a heat pump designed to handle Chicagoland’s cold winters, precise installation becomes the next crucial step. To ensure your system performs as expected, rely on ACCA Manual J calculations, verified by blower door tests, to determine your home’s heating and cooling requirements. Then, use ACCA Manual S to select equipment that aligns with those needs.
Cold climate heat pumps equipped with variable-speed inverter compressors are particularly effective because they adjust output to match heating and cooling demands. You can either size the system to cover 100% of your heating load at design temperatures (typically 0°F to 5°F in Chicagoland) or opt for a system that covers 80% of the load, supplemented by additional heat during extreme cold spells. Avoid oversimplified sizing tools or rules of thumb – they often result in oversized units that cycle on and off too frequently, leading to poor humidity control in summer.
Outdoor unit placement is equally important. Install the unit 12–18 inches above the ground to avoid snowdrifts, and ensure it has the manufacturer-recommended clearance for airflow. In areas prone to heavy snowfall, consider an elevated gravel bed to prevent ice buildup. Redirect meltwater away from walkways and your home’s foundation to avoid hazards. While proper installation is the foundation, regular maintenance is key to keeping your heat pump efficient during the winter months.
Winter Maintenance Checklist
Keeping your heat pump in top shape during the winter requires consistent care. Start with monthly filter checks during the heating season. Depending on usage, replace or clean filters every 1–3 months, using MERV 8–13 filters to strike a balance between good air quality and adequate airflow.
After snowstorms, clear snow and ice from the outdoor unit, especially the top and sides, to ensure the fan operates freely. If ice encases the unit, switch to "Emergency Heat" mode or pour warm (not hot) water over the coils. Avoid using sharp tools to remove ice, as these can cause irreversible damage.
"The heat pump will not work properly if it is covered in snow and ice. Either turn the thermostat to ‘Emergency Heat’ to remove the snow and ice, or pour warm water over the pump. Do not use hot water." – Nick Smith, Author, RasMech
Maintain a steady thermostat setting, limiting temperature setbacks to 2–4°F. Large swings in temperature can activate auxiliary electric resistance heat, which is far less efficient. While your heat pump operates with a COP (Coefficient of Performance) between 2.0 and 3.5 in mild winter conditions, resistance heat has a COP of about 1.0, making it more expensive to run. Short defrost cycles are normal, as the system reverses temporarily to melt frost on the outdoor coils. However, if defrost cycles become frequent or prolonged, or if heavy ice builds up, it may signal airflow or sensor problems that need professional attention.
Eco Temp HVAC Maintenance Services

For homeowners who prefer professional upkeep, service programs tailored to Chicagoland’s harsh winters can help ensure optimal performance. Regular maintenance is especially important for systems with advanced features like variable-speed inverter compressors and defrost cycles.
Eco Temp HVAC provides comprehensive maintenance plans designed for cold-weather efficiency. Their certified technicians handle monthly checks of electrical terminals, refrigerant charge measurements, and duct sealing to prevent heat loss. Semi-annual maintenance includes motor lubrication and belt inspections to keep the system running smoothly throughout the season.
Annual inspections focus on clearing system obstructions, testing electrical controls, and verifying efficiency under design temperature conditions. Eco Temp also offers 24/7 support in areas like Chicago, St. Charles, Bartlett, Lemont, Downers Grove, and Palatine, ensuring quick responses to winter emergencies. As a Mitsubishi Diamond Elite Contractor, they provide expert service for cold climate systems, with extended warranties up to 12 years on qualifying products.
Conclusion: Heat Pumps for Cold Climate Heating
Modern cold climate heat pumps have transformed how we heat our homes in winter. By transferring heat instead of generating it, these systems achieve 300% to 400% efficiency, even during harsh winters. This approach can cut electricity use for heating by as much as 75% compared to electric resistance systems.
Designed for sub-zero temperatures, ENERGY STAR models maintain impressive efficiency, delivering 70% to 100% of their nominal heating capacity even at 5°F. This ensures reliable warmth throughout Chicagoland’s freezing winters.
The benefits of heat pumps are widely recognized by experts:
"Because they transfer heat rather than generate heat, heat pumps can efficiently provide comfortable temperatures for your home." – U.S. Department of Energy
To get the best performance, proper installation and regular maintenance are key. Using ACCA Manual J load calculations ensures the system is sized correctly, while routine servicing prevents the 10% to 25% efficiency loss caused by neglect. For homeowners in Chicagoland, working with certified professionals who understand cold-weather requirements – like placing units above snowdrifts and fine-tuning defrost cycles – guarantees dependable performance all year long.
On top of that, federal tax credits covering up to 30% of installation costs make these systems even more appealing. With operating costs that often compete with or outperform natural gas, cold climate heat pumps offer an energy-efficient, cost-effective solution tailored to Chicagoland’s winters. They’re a smart investment for long-term comfort and savings.
FAQs
Will a heat pump keep my home warm below 0°F?
Absolutely. Modern heat pumps are designed to efficiently heat homes even when the thermometer dips below zero. Many models can handle temperatures as low as -15°F, and some continue to perform well around -20°F. This impressive capability comes from advanced technologies like variable-speed compressors and defrost systems, which help maintain consistent warmth even in the harshest winter conditions.
How do I know what size heat pump my home needs?
Properly sizing a heat pump for your home is key to maintaining comfort and efficiency. If the system is too small, it will struggle to meet your heating and cooling needs. Too large, and it may cycle on and off frequently, wasting energy and leading to uneven temperatures.
The best approach? Consult a professional HVAC technician. They’ll use tools like the ACCA Manual J to calculate your home’s heating and cooling requirements. This method takes into account factors like your home’s size, insulation levels, number of windows, and the local climate.
While online calculators and rough estimates might seem convenient, they often lack the precision needed to ensure your system performs well – especially in colder regions where sizing mistakes can have a bigger impact. Trust the experts for accurate results.
When should I use auxiliary or emergency heat?
When it comes to your heat pump, auxiliary or emergency heat is like a backup plan. It’s meant to kick in only when your heat pump struggles to keep your home warm. This can happen during extremely cold weather, when the system is malfunctioning, or during defrost cycles.
However, it’s important to remember: this feature is designed for temporary use in emergencies – not for everyday heating. Overusing it can lead to higher energy bills and unnecessary wear on your system.